16798.Listed below are four respiratory capacities (a - d) and four jumbled respiratory volumes of a normal human adult
Which one of the following is the correct matching of two capacities and volumes?
| Respiratory capacities | Respiratory volumes |
|---|---|
| (a) Residual volume | 2500 mL |
| (b) Vital capacity | 3500 mL |
| (c) Inspiratory reserve volume | 1200 mL |
| (d) Inspiratory capacity | 4500 mL |
Which one of the following is the correct matching of two capacities and volumes?
(a) 4500 mL, (b) 3500 mL
(b) 2500 mL, (c) 4500 mL
(c) 1200 mL, (d) 2500 mL
(d) 3500 mL, (a) 1200 mL
16799.Which one of the following statement is NOT correct regarding trachea?
It usually lies posterior to the muscular esophagus.
It splits into the right and left bronchi to supply air to the lungs
Opening to the trachea is covered by epiglottis.
Tracheal rings are C-shaped
16800.Plants whose requirement for respiration is similar to animals are
Algae
Fungi
Lichens
Cyanobacteria
16801.Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
Tuberculosis is caused by a rod-shaped bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis is highly infectious and can be spread by airborne droplets.
Tuberculosis cant be treated by antibiotics
In Pulmonary Tuberculosis the elasticity of lungs is reduced.
16802.During anaerobic respiration, one molecule of pyruvic acid
Losses 3 molecules of ATP
Losses 6 molecules of ATP
Gains 2 molecules of ATP
Gains 4 molecules of ATP
16803.Which one of the followings is NOT correct regarding Exhalation (expiration)?
Expiration is typically a passive process
Exhalation starts when the expiratory muscles relax
The elastic properties of the lung help to expel deoxygenated air during exhalation
During exhalation, elastic properties of the lung help to expel deoxygenated air
16804.Which one of the followings is correct regarding larynx?
It prevents foreign objects from entering the trachea
It houses the vocal cords
It is an organ made of cartilage and connects the pharynx to the trachea
All of these are correct.
16805.Which one of the following is a possibility for most of us in regard to breathing, by making a conscious effort?
One can consciously breathe in and breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone, without moving the ribs at all
The lungs can be made fully empty by forcefully breathing out all air from them
One can breathe out air totally without oxygen
One can breathe out air through eustachian tubes by closing both the nose and the mouth
16806.The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gases takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function?
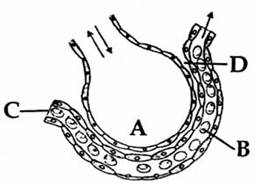

B : Red blood cell - transport of CO2 mainly
C : Arterial capillary - passes oxygen to tissues
A : alveolar cavity - main site of exchange of respiratory gases
D : Capillary wall - exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place here
16807.One gram mole of glucose on complete oxidation to CO2 and H2O produces about
686,000 cal
6,860 cal
6,860,000 cal
68,600 cal
16808.Cytochromes are
Electron acceptors
Protein acceptors
Oxygen acceptors
Passage – way for carbohydrates
16809.In respiration, pyruvic acid is
Formed only when the cell is with mitochondria
Formed only when oxygen is available
Formed only when cell is performing aerobic respiration
Commonly formed as intermediate product of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
16810.What ultimately occurs during respiration is
Synthesis of ATP
Electron transport
break down of ATP
capture of solar energy
16814.Mitochondrial component connected with ATP synthesis
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Matrix
F0 – F1 particles
16815.Mitochondrial criste are sites of
Kreb's cycle
Oxidation reduction reaction
Protein synthesis
Lipid synthesis
16816.Correct sequence in electron acceptors in ATP synthesis is
Cyt, a , a3, b, c
Cyt, b, c, a, a3
Cyt, c, b, a, a3
Cyt, b, c, a3, a
16819.The intermediate product of glycolysis which undergoes lysis or splitting is
Fructose 1-6 diphosphate
Dihydroxyacetone 3 phosphate
Glucose – 6 – phosphate
Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate
16820.Number of carbon atoms present in citric acid, oxaloacetic acid pyruvic acid are respectively
6, 3 and 3
6, 4 and 3
5, 4 and 3
6, 4 and 2
16821.Removal of hydrogen and CO2 from substrate is called
Oxidation
Decarboxylation
Reductive carboxylation
Oxidative decarboxylation
16822.Aerobic respiration of one glucose produces
12 NADH + 2FADH2 + 38 ATP
12 NADH + 30 ATP + H2O
8 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2ATP
10 NADH2 + 2 FADH2 + 2 ATP + 2 GTP
16824.End products of aerobic respiration are
Sugar and oxygen
Water and energy
Carbon dioxide and energy
Carbon dioxide, water and energy
16825.Incomplete oxidation of glucose into pyruvic acid with several intermediate steps is known as
HMS-pathway
TCA pathway
Glycolysis
Kreb's cycle
16826.Kreb's cycle begins with the reaction
Citric acid + Acetyl CoA
OAA + Acetyl Co-A
OAA + Citric acid
OAA + Pyruvic acid
16827.Formation of lactic acid from pyruvic acid requires
Reduction
Oxidation
Decarboxylation
Hydration
16828.When a pair of electron from NADPH2 is transported through respiration ETS, it results in the formation of
5 molecules of ATP
4 molecules of ATP
3 molecules of ATP
2 molecules of ATP
16829.In presence of cyanide, azide and carbon monoxide, the rate of respiration
Decreases
Increases
Remains the same
None of the above
16831.Oxidation step of glycolysis is
1,3 di PGA → 3 PGA
3 PGAL → 1, 3 diPGA
PGA → PEP
Fructose 1, 6 diphosphate → PGAl + DHAP
16833.Net gain of ATP molecules, during aerobic respiration is
36 molecules
38 molecules
40 molecules
48 molecules
16834.Total number of water molecules produced per molecule of glucose during aerobic respiration is
10
6
12
8
16835.Number of oxygen molecules required for glycolytic breakdown of one glucose molecule is
Three
Zero
Thirty eight
Six
16837.In aerobic respiration, first CO2 is liberated during
Oxidation of pyruvic acid
Decarboxylation of oxalosuccinic acid
Decarboxylation of a ketoglutaric acid
Alcoholic fermentation
16838.The maximum volume of air contained in the lung by a full forced inhalation is called
Vital capacity
Tidal volume
Total lung capacity
Inspiratory capacity
16839.Protoplasmic repiration is respiration
Occuring in protoplasm
Occuring in cytoplasm
when protein is respiration substrate
Occuring outside mitochondria
16841.Incomplete breakdown of sugars in anaerobic respiration forms
Glusoce and CO2
Alcohol and CO2
Water and CO2
Sucrose and water
16842.The number of molecules of pyruvic acid formed from one molecule of glucose at the end of glycolysis is
1
2
3
4
16844.Oxysome is made up of
Stalk, head piece and tail piece
Stalk, head piece and base piece
Head as basal piece
Stalk and head piece
16845.FADH2 is formed in conversion of
Succinyl CO-A succinic acid
Succinic acid-fumaric acid
Fumaric acid-malic acid
Isocitric acid-oxalosuccinic acid
16846.Muscle cell starved of oxygen and supplied with pyruvic acid will produce
CO2 only
Lactic acid
Ethonal
CO2 and H2O
16847.Respiratory center is located in the ________.
Pneumotaxic center
Medulla oblongata
Alveoli
Apneustic center
