Given, ABC is an equilateral triangle
And D is a point on side BC such that BD = $\dfrac{1}{3BC}$
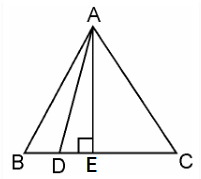
Let the side of the equilateral triangle be a, and AE be the altitude of ΔABC
BE = EC = $\dfrac{BC}{2} = \dfrac{a}{2}$
And, AE = $a\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
Given, BD = $\dfrac{1}{3BC}$
BD =$\dfrac{a}{3}$
DE = BE – BD = $\dfrac{a}{2} – \dfrac{a}{3} = \dfrac{a}{6}$
In ΔADE, by Pythagoras theorem
$AD^2 = AE^2 + DE^2$
$AD^2 = (\dfrac{a\sqrt{3}}{2})^2 + (\dfrac{a}{6})^2$
$AD^2 = \dfrac{3a^2}{4} + \dfrac{a^2}{36}$
$AD^2 = \dfrac{28a^2}{36}$
$AD^2 = \dfrac{7}{9} AB^2$
$9 AD^2 = 7 AB^2$